Hyundai India IPO is tentatively scheduled to open on 14 October and will instantly get into the record books, most notably being the biggest IPO in India. Although the Indian arm of the Korean automaker is a well-known brand and much has been said about its products, it is important to assess it from the IPO perspective. Here, we try to do the same through Hyundai IPO SWOT Analysis. Read on for more.

Hyundai IPO SWOT Analysis
Hyundai IPO Strength: Second Largest Auto OEM in India
As mentioned above, Hyundai Motor India is a well-known name and has claimed the title of second largest auto OEM in the Indian passenger vehicles market since Fiscal 2009 in terms of sales volumes. The company has consistently been the largest auto OEM in India by sales volume in the mid-size SUV sub-segment from Fiscal 2019 to the first 11 months of Fiscal 2024. Creta had a market share of 30% in the mid-size SUV sub-segment while Verna was the top-selling model in the premium sedans sub-segment with 31.2% market share, in the first 11 months of Fiscal 2024.
The company has been India’s largest exporter of passenger vehicles from Fiscal 2005 to the first 11 months of Fiscal 2024. Since its inception and up to December 31, 2023, Hyundai Motor India exported 3.53 million passenger vehicles to over 150 countries, including countries in Latin America, Africa, the Middle East, and Asia. The export market is a revenue driver for the company as it earns a higher average selling price (ASP) for exports versus domestic products.
Hyundai IPO Strength: Diverse Portfolio of Passenger Vehicles
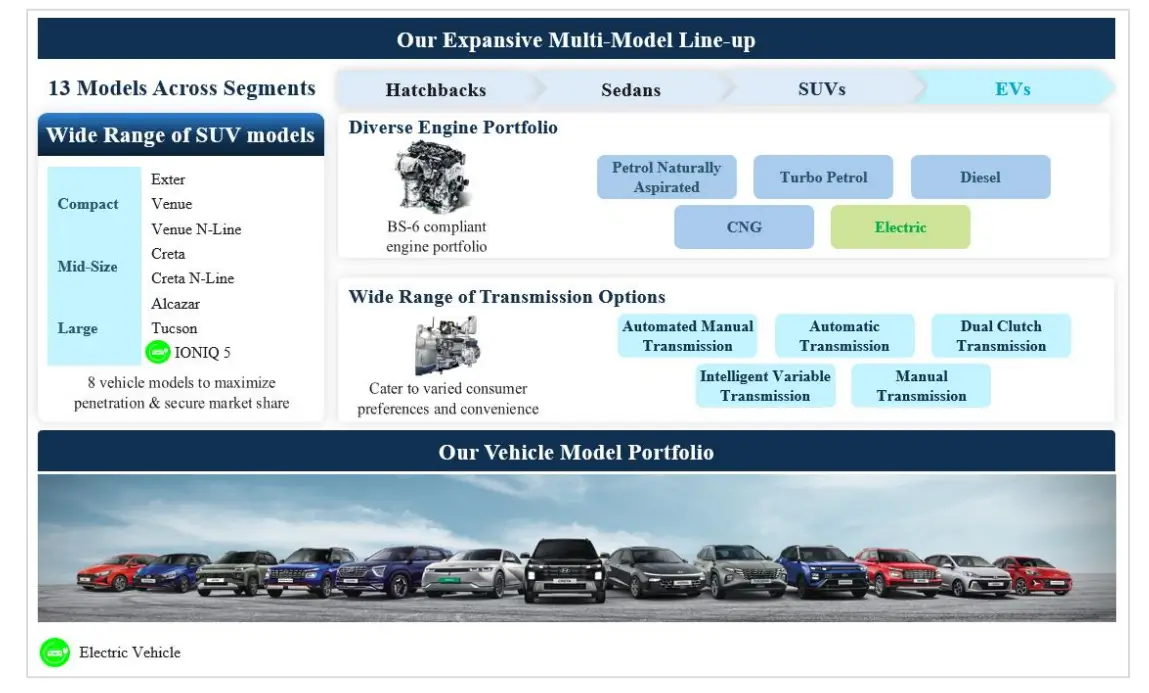
Hyundai Motor India has a wide portfolio of passenger vehicles that offer “something for everyone”. This portfolio consists of 13 passenger vehicle models across segments, including sedans (Aura and Verna), hatchbacks (Grand i10 NIOS, i20 and i20 N Line) and SUVs (Exter, Venue, Venue N Line, Creta, Creta N Line, Alcazar, Tucson and IONIQ 5).
Hyundai’s product diversity percolates down to engine and transmission options. Various passenger vehicle models have multiple engine fuel options across petrol, diesel, CNG, and EV along with diverse transmission options (MT, AMT, AT, DCT, and iVT).
Hyundai India IPO Strength: Identification of Emerging Market Trends
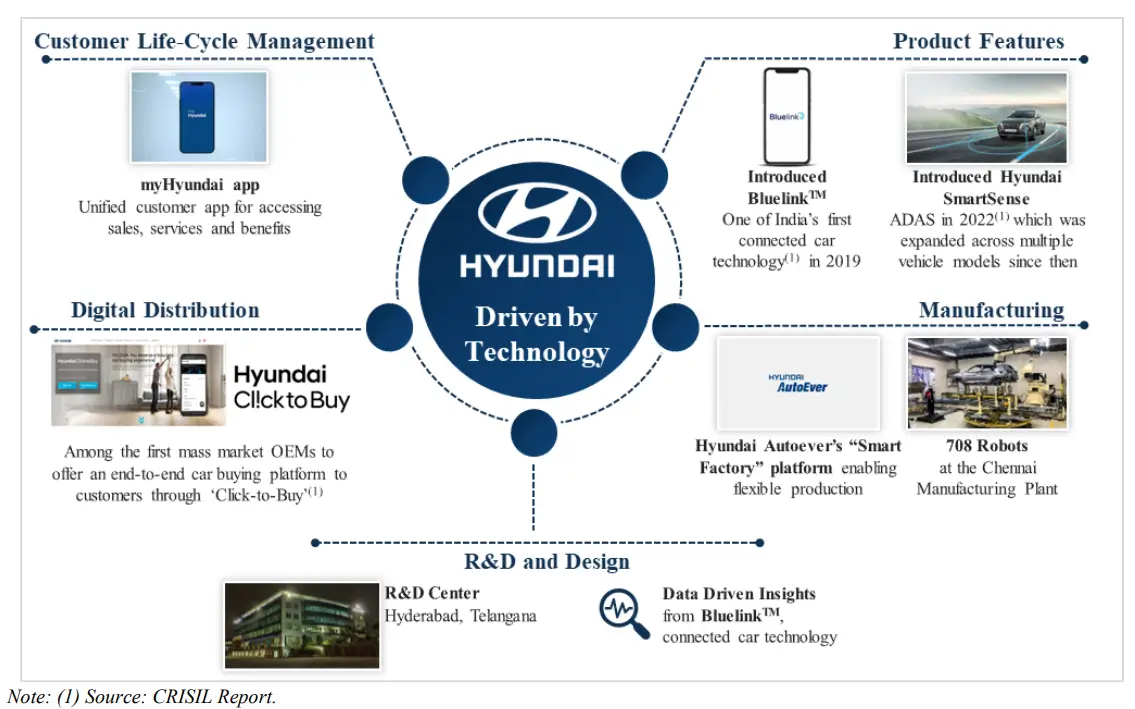
Hyundai Motor India identifies emerging market trends, latent customer needs and aspirations based on in-depth market and product research and gets suitable help from Hyundai Motor Company’s (HMC’s) global network. The company’s R&D centre in Hyderabad works closely with HMC’s centralized R&D hub in Namyang, Korea. This centre in Hyderabad is being expanded to become the hub for global compact passenger vehicle R&D for HMC. The company’s subsidiary, Hyundai Motor India Engineering, provides technical expertise to support local customization.
Hyundai Motor India tailors these global technologies and features to meet customer needs, designs, and preferences. The company introduced technologies such as the Bluelink voice recognition system to understand Hinglish (Hindi-English), it can support embedded voice commands without an internet connection, audio-video navigation & telematics. Based on market demand and customer preference, the company releases upgrades and model changes such as (i) upgrades in approximately four years and (ii) new full model change in approximately six years.
An example of the company’s early identification of market trends is the timely introduction of compact sedans and SUVs. Similarly, Hyundai was a pioneer in automatic and semi-automatic transmissions in India.
Hyundai IPO Strength: Pan-India Sales, Distribution and After-Sale Services Network
As of December 31, 2023, the company had 1,366 sales outlets across 1,031 cities and towns in India and 1,550 service centres across India in 962 cities and towns in India. Hyundai’s sales and service network was the second largest in India in terms of the number of customer touchpoints as of March 31, 2023. The company introduced a “Doorstep Service Programme” in 2020 to provide after-sale services to customers across primary rural markets and emerging cities through mobile service vans. The company has also launched a car maintenance programme “Hyundai Shield of Trust”, which covers the replacement of wear and tear parts. Customers can use the myHyundai app to access connected car features, book after-sale and maintenance services, renew or extend warranties and receive support from a 24/7 call centre, among other services.
Hyundai IPO Strength: Flexible and Automated Manufacturing Capabilities
Hyundai Motor India operates two manufacturing plants located in Chennai, Tamil Nadu and one under redevelopment in Talegaon, Maharashtra. The Chennai manufacturing plant is one of India’s largest single-location passenger vehicle manufacturing plants in terms of production capacity. The company’s passenger vehicles are based on five different platforms (four for internal combustion engine (ICE) passenger vehicles and one for EVs.
To enhance operational efficiency, Hyundai Motor India has a common platform architecture across the two manufacturing plants in Chennai and this enables manufacturing of eight different models in one plant and six different models in the other plant, with one model manufactured in both plants. As a result, based on market demand, selected models can be produced on multiple lines in parallel. This flexibility of having a common platform architecture lowers product development costs, reduces time-to-market, streamlines the manufacturing process, allows higher capacity utilization, and boosts agility in delivering new models.
The company’s manufacturing operations are highly automated, producing 131 passenger vehicles per hour, with a production rate of one passenger vehicle within 30 seconds. As of 31 March 2024, over 2,000 critical machines were connected with technologically advanced systems and 708 robots. This advanced manufacturing technology includes the integration of a vision system that confirms sealer application, enhancing efficiency and accuracy, and the four-layer painting process.
Hyundai IPO SWOT Analysis
Hyundai IPO Weakness: Raw Material Price Increase
Hyundai Motor India sources parts such as trims, engines and transmissions, and steel for manufacturing operations from a combination of domestic and foreign suppliers. The company’s operations and suppliers’ ability to provide parts and materials is affected by global commodity prices, inflation and the ability to negotiate with other suppliers effectively.
Hyundai IPO Weakness: Dependency on Suppliers
The company depends on a limited number of suppliers for the procurement of parts and materials. For nine months of Fiscal 2024, the top 5 suppliers of the company accounted for nearly 44% of parts and materials costs. Any failure by suppliers to provide parts and materials on time or at all, or as per specifications and quality standards for reasons such as capacity limitations, breakdowns, mould or machine failures, industrial relations and safety issues, could harm the company’s ability to meet manufacturing and delivery schedules.
Hyundai IPO Weakness: Overlap with Kia
Two of HMC’s group companies, Kia Corporation and Kia India Private Limited, are in a similar line of business as Hyundai Motor India which may involve a conflict of interests, which could adversely impact the business.
Hyundai IPO Weakness: Dependency on the Sales of SUV
The company depends on the sales of SUVs a substantial part of the revenue from the business comes from the sales of SUV vehicles. Any decrease in the demand for or disruption in the manufacturing of SUVs, or any other passenger vehicle models the company relies on in the future, could adversely impact operations.
Hyundai IPO SWOT Analysis
Hyundai IPO Opportunities: Outlook and Expectations
CRISIL expects the macroeconomic scenario to lend support to the industry growth with GDP projected to grow at a healthy pace between Fiscal 2024 to Fiscal 2029. India’s GDP growth is expected to outperform other major geographies in the next 5 years with an expected growth rate of 6-8%. India’s inflation levels are also expected to remain subdued in the 3-5% range. Fuel prices are also expected to remain near steady in the next 5 years. These favourable macroeconomic factors are expected to aid the consumer disposable income levels and propel the passenger vehicle industry forward.
Additionally, OEMs are expected to continue with launches of feature-rich competitively priced vehicles aiding the overall demand growth. The government’s push for scrapping old vehicles is expected to help in shortening replacement cycles and hence aid demand. CRISIL MI&A expects the industry to clock 4.5-6.5% CAGR between Fiscal 2024 to Fiscal 2029 period to reach 5.2-5.7 million domestic vehicle sales.
Growth in the domestic industry is expected to be led by the SUV and MPV segments while the hatchbacks, sedans and vans segments are expected to clock muted growth going ahead. All of the above-mentioned expectations and outlooks indicate positive growth in the Auto Industry while adding to Hyundai IPO Opportunities.
Hyundai IPO SWOT Analysis
Hyundai IPO Threats: Demand, Supply and Increased Competition
While the company has scored well so far on most points, there are some threats as well. India’s GDP growth is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6% to 8% between Fiscal 2024 and Fiscal 2029. Any moderation in GDP growth may have an impact on the incomes of people at large and hence the decision to buy passenger vehicles. This could be on account of an adverse monsoon that could adversely affect farm-related incomes, rural sentiments, food prices and thereby inflation. The resulting interest-rate hike could reduce the liquidity conditions thereby impacting the cost of purchase.
The Automobile industry is highly dependent on imports of raw materials. Commodity prices and prices of precious metals are impacted by geopolitical tensions and extreme weather shocks, which impact the input costs for OEMs. The INR/USD exchange rate also directly impacts the input costs and fuel prices. A weak INR exchange rate puts the burden on OEMs to decide whether or not to pass on the costs to the consumer. Often these fluctuations are absorbed by the OEMs which may negatively impact their overall margins. The competitive intensity in the automotive industry is expected to increase with easing import duties, PLI schemes and FDI norms that will encourage foreign passenger vehicle OEMs to enter India. There could be a possibility of these players entering the Indian passenger vehicle market in the future as well. Hence competitive risk will be high.